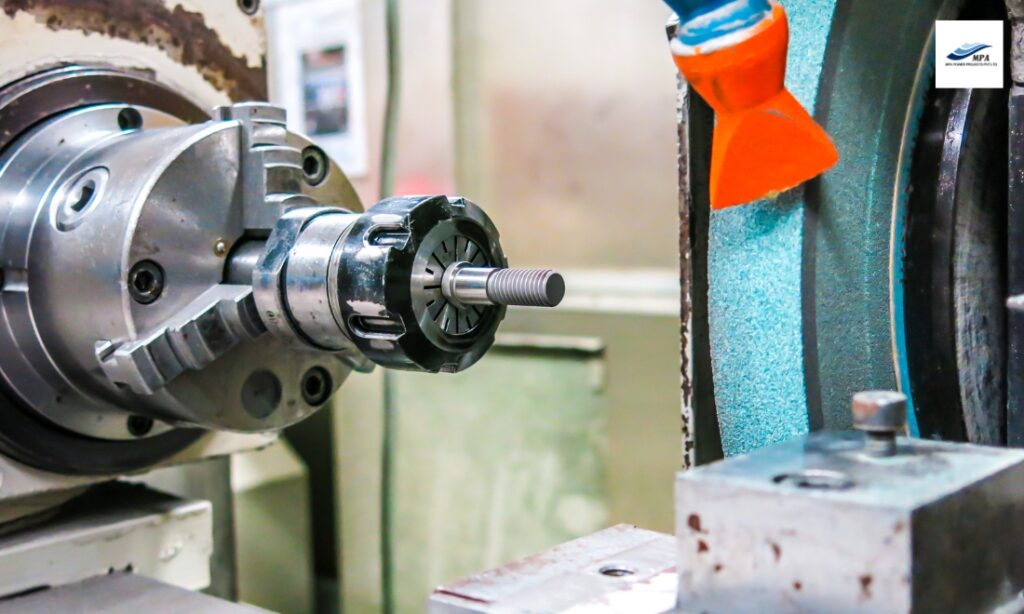
The essential parts of spinning machinery, rotor shafts need to be balanced and precisely positioned in order to function at their best. A critical step in both production and maintenance, rotor shaft grinding entails scraping material from the shaft’s surface in order to produce the correct dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes. This complex procedure ensures that the shaft runs effectively and dependably by fusing the science of engineering with the art of accuracy.
Understanding Rotor Shafts
What is a rotor shaft?
Mechanical cylinders transfer torque and velocity forces as rotor shafts. Electricity and aircraft are a couple of examples of industries utilizing them to join rotating parts and enable them to transfer operating. Plan and design rotor shafts with operating forces in consideration. Weights, vibrations, and thermal expansion are operators under forces.
Common Issues with Rotor Shafts
Wear and tear: Surface wear changes the diameter size and surface area of the shaft gradually.
Corrosion:
External factors can introduce corrosion, wearing away items.
Misalignment: Bearings and other parts are likely to wear out in the event that you do not align them or when you use them for some time.
Surface Defects: Faulty surfaces: Defects such as scratches, pitting, and nicks are likely to decrease the speed of the machine.
The work of repairing the rotor shaft grinding is to ensure the spoil has not happened much and restore long-term operation.
The Grinding Process
Steps in Rotor Shaft Grinding
There are numerous stages that are mandatory in the repair of the rotor shaft grinding or Compressor Shaft Grinding:
Inspection
Before cutting, technicians inspect rotor shaft damage and wear. This is critical to determining where the repairs will be made. Shaft measurements are taken with micrometers and calipers. Changes planned for the shaft are checked for errors and corrected before grinding is performed.
Setup
The rotor shaft is safely mounted in the grinding machine. Setup of the machine is critical to maintaining shaft position while grinding. A smooth, even grind significantly affects shaft performance and lifespan, so balancing is critical.
Grinding
The dirt is removed from the shaft through a careful grinding procedure with a grit wheel. Depending on the assessment of the shaft material and wear, the choice is made based on the grit used and the grinding procedure applied. This will slowly bring the shaft back to its original size as the surface imperfections are removed to allow a fit and function.
Finishing
The finishes are smooth and of standard size after grinding. These are the last procedures that ensure the shaft is technically correct, therefore enhancing the performance and life expectancy.
Final Inspection
Afterward, it is carried out with the shaft for grinding and polishing, and finally, it is tested. The grinding and testing determine that there do not exist any faults and that all the features of the shaft do meet the criteria. All the characteristics must be included within the least space for field reliability.
Precision and tolerance
Grinding is very precise; small defects will ruin the implementation of the shaft. If mechanical problems are to be avoided, such as overheating or stressed components, there exist tolerances both in diameter and ends. These are preferably produced using high-precision grinding techniques.
Advantages of Rotor Shaft Grinding
Restoring Functionality
Rotor shaft grinding can indeed cure. This process restores the functionality of the shaft system by eliminating worn areas and surface defects. Well-finished rotor shafts add improved balance and spinning speed for better machine performance.
Extending Equipment Life
There are the outcomes of a clean rotor blade from regular cleaning. Increased machine life would result from preventive maintenance. The cost of long hours of machine downtime and the replacement of systems can be kept at a minimum by preventing wear and tear. More return on investment equates to longer years of equipment life.
Cost-Effectiveness
This certainly makes the rotor shaft grinding much more affordable than buying new tools or replacing shattered shafts. Reparations reduce scrap and maximize resources, reducing machine breakdowns, thus decreasing maintenance while increasing performance.
The Role of Expertise in Rotor Shaft Grinding
The Importance of Skilled Technicians
Despite the use of high-technology instruments and processes involved in the Rotor Shaft Grinding Onsite process, it is not possible without the aid of technicians. Experienced professionals can look at a shaft and determine the best grinding process that needs to be done. Data analysis of the best practices and unexpected issues that crop up affect grinding.
Training and Experience
This becomes a never-ending practice of studying and practicing. The technicians must be aware of the current procedures. They must also have awareness about the industry-specific rotor shaft specifications. Various information enables one to tackle the difficulties and perform accomplished work.
Applications of Rotor Shaft Grinding
Industries Benefiting from Rotor Shaft Grinding
The rotor shaft grinding aids a variety of companies by preserving the performance and life of a device. Some of such instances are:
Power Generation
Rotor shafts are the ones producing energy either in turbines or in engines; these components work perfectly with rotating shafts. Rotor blades stay sharp always due to regular grinding and maintenance. This type of maintenance serves to eliminate the chance for wear and tear to decrease efficiency or result in failure, ensuring electricity output.
Aerospace
Aerospace jet engines require accurate rotor shafts. The safety and efficiency of such engines rely on the spinning shaft, to be precise. It is vital to the safety of the engine that they have periodic shaft grounding and maintenance in order to run planes safely. In aeronautics, precision grinding is called for to ensure that issues of performance and safety for shafts are dealt with.
Manufacturing
Lathes, mills, and precision gearmakers use rotor shafts. These rods monitor the speed of machinery and its performance. Industrial equipment rotor blades are regularized and improved using ground items. Proper care of the shaft reduces failures, prolonging the lifespan to improve industrial efficiency.
Case Studies
Industrial equipment’s rotating shaft was shaking and running poorly due to its rough surface. After testing and grinding the shaft back to size and quality, the facility reported operational stability improved and energy consumption lowered.
Another example from the aerospace industry is the cutting of rotor shafts for the maintenance of an aircraft’s engine. The rotor blades were precision ground to enhance engine performance and to facilitate its maintenance process.
Challenges in Rotor Shaft Grinding
Even though it has several advantages, rotor shaft grinding is a difficult process. The technicians need to consider
Material Selection
Material selection is involved in grinding because different materials react to various harsh circumstances. Select grinding methods and abrasives based on hardness, toughness, and heat conductivity. Many materials need special grinding wheels or cooling methods to avoid scorching, bending, or other damage. If they understand material behavior, technicians can work without damaging it.
Noise and vibration
Grinding can be noisy, thus disturbing the workplace. Control these for the comfort and safety of the workers. Noise can harm hearing, and excessive vibrations can cause damage to gears and hinder grinding. Noiseproofing and vibration dampening enhance the quality and safety of work.
Resource Allocation
It means balancing price, precision, and downtime. With great demand and strict production schedules, it is often hard to achieve fine results without overspending or wasted time. Choose the right tool, sharpen the right way, and manage maintenance for maximum utilization of resources with no interruptions to the production line. Balance impacts output and the long-lasting grinding success.
Conclusion
Overall, rotor shaft grinding is an art and science of preserving gear functionality and durability. Two-sided grinding to technical precision improves usefulness and prolongs tool life. The application of rotor shaft grinding is vast and ranges in every industry. Training and state-of-the-art technology can enhance this very essential maintenance routine to keep equipment working smoothly for years.









No Comments